Jupiter
Satellites
- Europa
- Io
- Ganymede
- Callisto
- Amalthea
- Himalia
- Thebe
- More...
- Radius: 3,959 miles
- Distance From Sun: 483,800,000 miles
- Mass: 1.898E27 kg
- Gravity: 24.79 m/s²
- 1 Day: 0d 9h 56m
- Orbital Period: 12 years
- Population: 0 confirmed
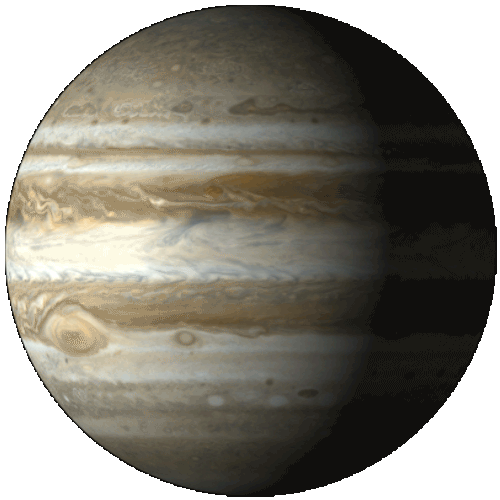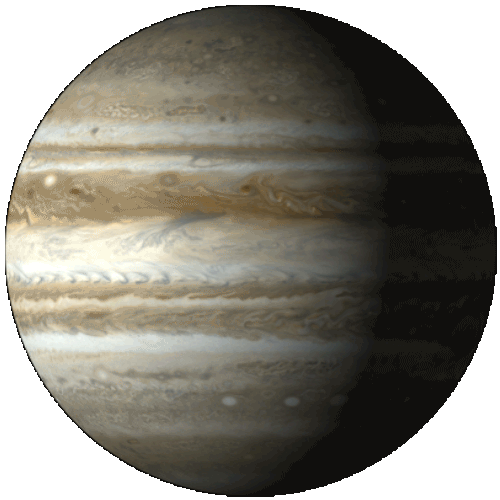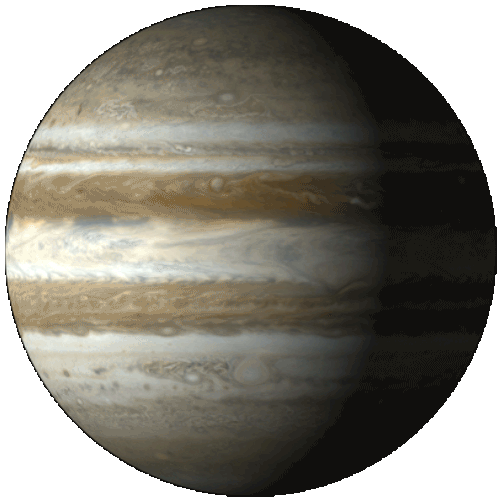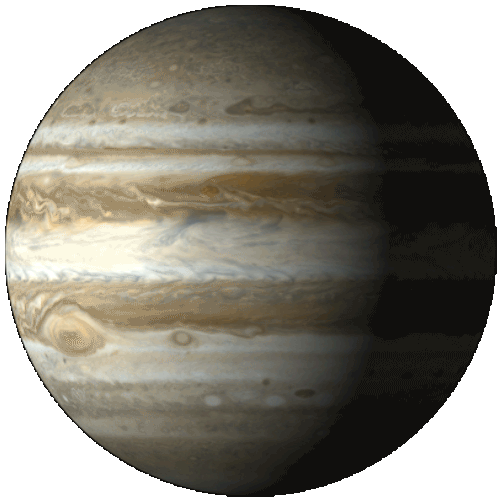
Jupiter
The fifth planet from the Sun and the largest planet in the Solar System.
It is a giant planet with a mass one-thousandth that of the Sun, but is two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined. Jupiter is a gas giant, along with Saturn (Uranus and Neptune are ice giants). Jupiter was known to astronomers of ancient times. The Romans named it after their god Jupiter. When viewed from Earth, Jupiter can reach an apparent magnitude of −2.94, bright enough to cast shadows, and making it on average the third-brightest object in the night sky after the Moon and Venus.
Jupiter is primarily composed of hydrogen with a quarter of its mass being helium,
although helium only comprises about a tenth of the number of molecules. It may also have a rocky core of heavier elements, but like the other giant planets, Jupiter lacks a well-defined solid surface. Because of its rapid rotation, the planet's shape is that of an oblate spheroid (it has a slight but noticeable bulge around the equator). The outer atmosphere is visibly segregated into several bands at different latitudes, resulting in turbulence and storms along their interacting boundaries. A prominent result is the Great Red Spot, a giant storm that is known to have existed since at least the 17th century when it was first seen by telescope. Surrounding Jupiter is a faint planetary ring system and a powerful magnetosphere. Jupiter has at least 67 moons, including the four large Galilean moons discovered by Galileo Galilei in 1610. Ganymede, the largest of these, has a diameter greater than that of the planet Mercury. Ganymede Io Europa Callisto There have been several explorations by robotic spacecraft, most notably during the early Pioneer and Voyager flyby missions and later by the Galileo orbiter. The most recent probe to visit Jupiter was the New Horizons spacecraft in late February 2007 en route to Pluto, using the gravity from Jupiter to increase its speed and bend its trajectory. Future targets for exploration in the Jovian system include the possible ice-covered liquid ocean on the moon Europa. Galilean Moons







